A Deep Dive into Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Introduction:
The Rise of Automation in a Digital Era
In the dynamic landscape of the digital age, organizations are continually seeking innovative solutions to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and stay competitive. One such transformative force making significant strides in this domain is Robotic Process Automation (RPA). RPA represents a paradigm shift in the way businesses conduct routine, rule-based tasks by deploying software robots to automate processes. This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricate realm of RPA, unraveling its key principles, applications across industries, potential benefits, challenges, and the evolving landscape of automation in the workplace.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Unleashing Digital Workers
At its core, Robotic Process Automation is a technology that employs software robots or “bots” to emulate human actions in executing repetitive, rule-based tasks within digital systems. These bots interact with existing applications and systems by leveraging user interfaces, making them versatile tools capable of navigating a myriad of processes across different platforms.
- Key Principles of RPA:
- Rule-Based Automation: RPA excels in automating tasks governed by clear, rule-based instructions. This can include data entry, data extraction, report generation, and more.
- User Interface (UI) Interaction: Bots interact with applications just like humans, using the existing UI elements such as buttons, dropdowns, and input fields.
- Non-Invasive Integration: RPA does not require changes to existing IT infrastructure. It operates as a layer on top of existing systems, making implementation relatively non-disruptive.
- Applications Across Industries:
- Finance and Accounting: Automation of invoice processing, reconciliation, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources: Streamlining onboarding processes, payroll automation, and employee data management.
- Customer Service: Automating responses to routine inquiries, updating customer records, and managing ticketing systems.
- Healthcare: Claims processing, appointment scheduling, and data entry.
- Supply Chain Management: Inventory management, order processing, and logistics coordination.
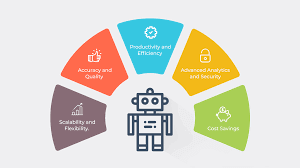
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation: Transformative Impact on Businesses
The adoption of RPA brings forth a myriad of benefits, positioning it as a transformative force in the realm of business operations. Understanding these advantages is essential in comprehending the allure of RPA for organizations seeking to optimize their workflows.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Accuracy:
- Bots tirelessly execute tasks without succumbing to fatigue or errors, ensuring consistently high accuracy and speed.
- Reduction in processing time leads to improved operational efficiency and faster delivery of services.
- Cost Savings and Resource Allocation:
- RPA eliminates the need for manual intervention in routine processes, leading to significant cost savings in labor.
- Human resources can be redirected to more strategic, value-added tasks that require creativity and critical thinking.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
- RPA systems are inherently scalable, allowing organizations to expand automation efforts as needed.
- Bots can adapt to varying workloads, providing flexibility in handling fluctuations in demand.
- Improved Compliance and Audit Trail:
- RPA ensures consistent adherence to predefined rules and regulations, reducing the risk of human error in compliance-related tasks.
- The automated nature of RPA processes facilitates the creation of detailed audit trails for regulatory purposes.
- Enhanced Customer Experience:
- Faster response times and error-free processing contribute to an improved customer experience.
- Customer-facing processes, such as order fulfillment and query resolution, can benefit from the efficiency gains enabled by RPA.
- Data Accuracy and Integration:
- RPA systems operate with a high degree of accuracy, minimizing data entry errors.
- Integration capabilities allow bots to interact seamlessly with diverse applications, fostering data consistency across the organization.
Challenges and Considerations: Navigating the Automation Landscape
While the benefits of RPA are substantial, organizations must also navigate challenges inherent in the adoption and implementation of automation technologies.
- Complexity of Processes:
- Certain processes may be too complex or unstructured for automation, requiring human intervention.
- Identifying suitable processes for automation is crucial to realizing the full potential of RPA.
- Initial Implementation Costs:
- While RPA promises long-term cost savings, the initial implementation can involve significant expenses, including software licensing, training, and infrastructure upgrades.
- Change Management and Workforce Impact:
- Introducing automation may necessitate changes in organizational structures and workflows, impacting existing job roles.
- Successful RPA adoption requires effective change management strategies to ensure a smooth transition for the workforce.
- Security and Compliance Concerns:
- The interaction of bots with sensitive data raises security concerns. Organizations must implement robust security measures to safeguard against potential risks.
- Compliance with industry regulations becomes paramount, necessitating careful design and monitoring of automated processes.
- Maintenance and Upkeep:
- Regular maintenance of RPA systems is essential to address updates, changes in underlying systems, and evolving business requirements.
- Ensuring ongoing alignment with organizational goals is crucial for sustained success.
Evolution and Future Trends in RPA: Embracing Intelligent Automation
The landscape of RPA is dynamic, with continuous advancements and innovations shaping the future trajectory of automation technologies.
- Cognitive Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Integration of RPA with AI technologies, enabling bots to perform more complex tasks that involve decision-making and cognitive abilities.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) augment RPA capabilities for greater adaptability.
- Hyperautomation:
- A holistic approach that combines RPA with complementary technologies such as process mining, analytics, and AI to create end-to-end automation solutions.
- Hyperautomation aims to automate entire business processes, driving increased efficiency and effectiveness.
- Human-Robot Collaboration:
- Emphasis on collaboration between human workers and bots to create a synergistic work environment.
- Bots handle repetitive, mundane tasks, allowing humans to focus on strategic, creative, and high-value activities.
- Automation as a Service:
- Cloud-based RPA solutions and automation platforms offered as a service, allowing organizations to leverage automation without heavy upfront investments.
- Increased accessibility and scalability are key features of automation as a service.
- Focus on Analytics and Insights:
- Integration of analytics tools with RPA systems to provide actionable insights and data-driven decision-making.
- Enhanced analytics capabilities contribute to continuous process improvement.
- Expanded Industry Applications:
- RPA extends its reach to new industries, including sectors such as legal, marketing, and education.
- Customization of RPA solutions for specific industry requirements becomes more prevalent.
Conclusion: Embracing the Automated Future
In the closing chapters of this exploration into the realm of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), it becomes evident that we stand at the crossroads of a profound transformation. The narrative of RPA transcends the mere adoption of a technology; it articulates a narrative of organizational evolution, where the mundane is automated, and the workforce is liberated to engage in strategic, value-driven pursuits.
As we reflect on the journey through the intricacies of RPA—from its fundamental principles to its far-reaching applications across industries—we witness the unfolding of a digital revolution. RPA has transcended its role as a mere efficiency tool; it has become the vanguard of a paradigm shift in the way businesses perceive and execute their operations. The benefits of enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings, highlighted in the earlier chapters, underscore RPA’s position as a cornerstone of contemporary business strategy.
Navigating the challenges and considerations of RPA implementation becomes a crucial aspect of this journey. Organizations, as they embark on the path of automation, must recognize that the integration of technology is not without its complexities. From managing workforce transitions to addressing security and compliance concerns, the successful adoption of RPA requires a holistic approach—one that involves not just technology but also embraces change management, continual learning, and a commitment to adaptability.
The future trends in RPA unveil a landscape where human and digital workers harmoniously collaborate, leveraging the collective strengths of cognition, adaptability, and efficiency. The convergence of RPA with artificial intelligence, the concept of hyperautomation, and the emphasis on human-robot collaboration signal a future where the workforce is augmented by technology rather than replaced by it. In this automated future, organizations will not merely survive; they will thrive by unlocking unprecedented levels of innovation and strategic thinking.
The story of RPA is a story of empowerment. It empowers organizations to reallocate human resources to tasks that demand creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence—qualities that remain irreplaceable by automation. It empowers employees to transcend routine, repetitive tasks, allowing them to contribute meaningfully to the organization’s objectives. Most importantly, it empowers industries to adapt to the evolving digital landscape, fostering resilience, agility, and a competitive edge.
As we pen the conclusion to this exploration, the narrative of RPA resonates with the broader story of technological evolution. The digital future is not a distant horizon; it is the reality we navigate today. Organizations that embrace the potential of RPA are not just adopting a technology; they are embracing a philosophy—an ethos that champions progress, efficiency, and the continual pursuit of excellence.
In the ever-accelerating symphony of technological innovation, RPA emerges as a key melody—a transformative force that harmonizes the rhythm of automation with the melody of human ingenuity. The chapters written by organizations pioneering RPA adoption are chapters of resilience, adaptability, and a commitment to sculpting a future where the workforce and technology coalesce in a resounding crescendo of success.
As we turn the page towards the automated future, the narrative of RPA beckons organizations to be not mere readers but active authors, shaping the contours of a future where the boundaries between the conceivable and the achievable blur into a seamless narrative of progress. The story of Robotic Process Automation is not just a tale of digital bots and automated processes; it is a narrative of transformation—a journey where organizations transcend limitations, empower their workforce, and script a future where efficiency is not just a goal but a way of organizational life.
Related Posts

Cosmos: Building the “Internet of Blockchains”

Navigating the Web3 Frontier: A Deep Dive into Privacy Protocols