Navigating the Landscape of Web 3.0: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the Landscape of Web 3.0: A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving realm of the internet, each new iteration brings forth transformative changes that shape the digital landscape. Enter Web 3.0, a paradigm shift poised to revolutionize the way we interact with the online world. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the intricacies of Web 3.0, exploring its defining characteristics, underlying technologies, potential applications, and the implications it holds for individuals and businesses alike.
Understanding Web 3.0:
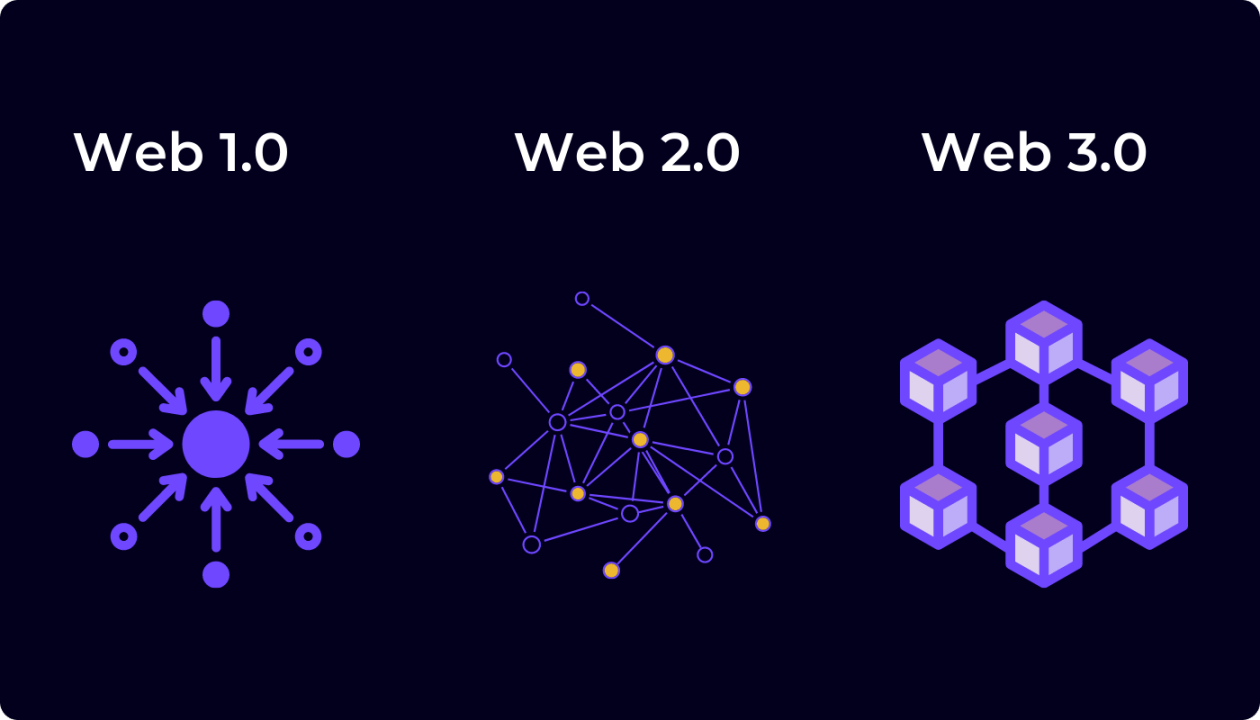
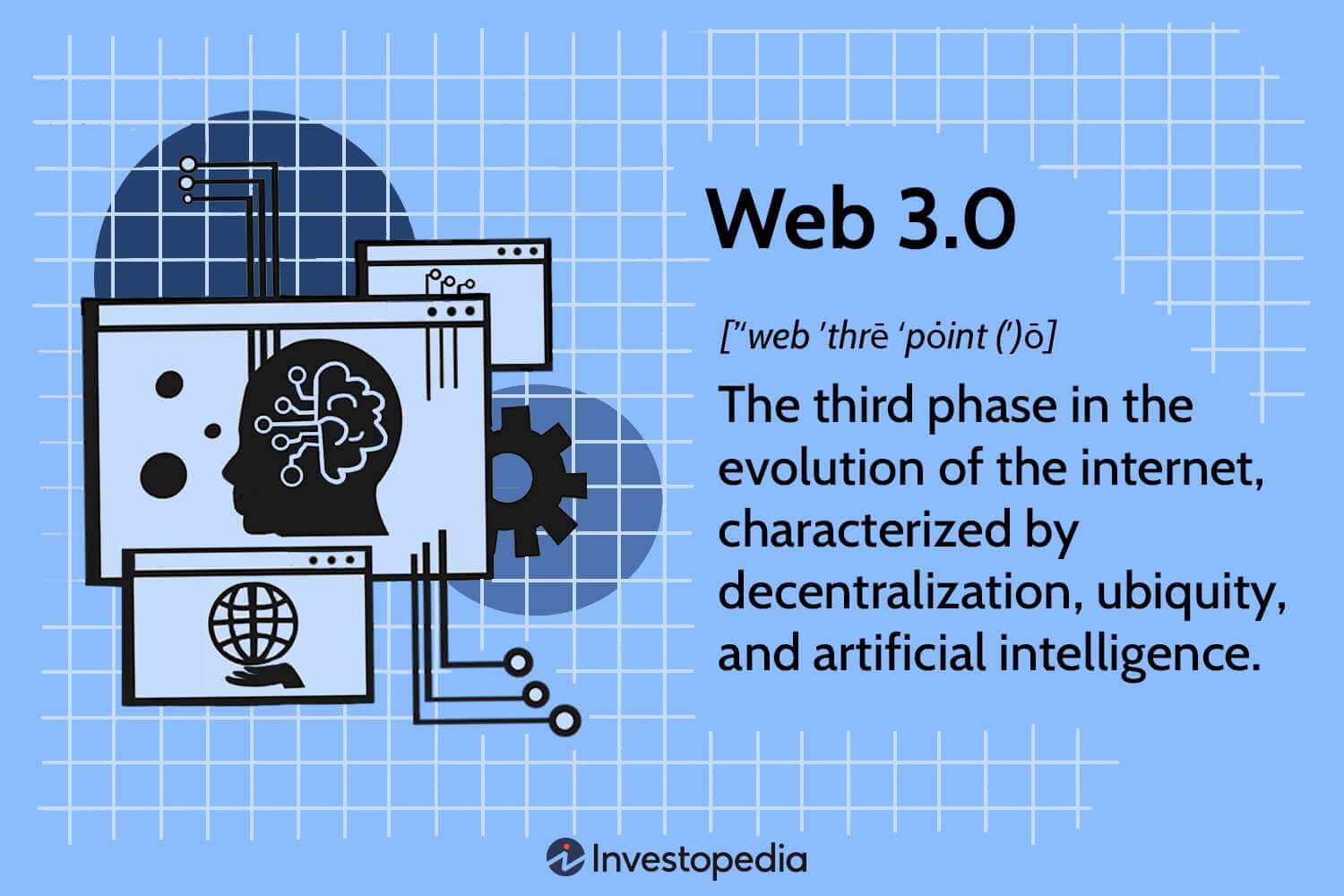
At its core, Web 3.0 represents the next phase of internet evolution, characterized by decentralized architectures, interoperability, and enhanced user empowerment. Unlike its predecessors, which primarily relied on centralized platforms and siloed data, Web 3.0 embraces decentralized protocols such as blockchain and peer-to-peer networks to foster greater transparency, security, and user control.
Key Features of Web 3.0:
- Decentralization: One of the defining features of Web 3.0 is its decentralized nature, which eliminates the need for intermediaries and central authorities. Instead of relying on single points of control, data and services are distributed across a network of nodes, ensuring greater resilience and censorship resistance.
- Interoperability: Web 3.0 aims to break down the barriers between disparate systems and platforms, enabling seamless interoperability and data exchange. By adopting open standards and protocols, users can access and interact with a diverse array of applications and services across the web.
- Data Ownership: In the Web 3.0 paradigm, individuals have greater ownership and control over their personal data. Through cryptographic techniques such as public-private key pairs and decentralized identity systems, users can securely manage their digital identities and selectively share data with trusted parties.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, play a pivotal role in Web 3.0 ecosystems. Powered by blockchain technology, smart contracts enable automated and trustless transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and streamlining business processes.
- Tokenization: Web 3.0 embraces the concept of tokenization, wherein assets and digital representations of value are represented and exchanged as tokens on blockchain networks. This enables new forms of value creation, ownership, and monetization, unlocking opportunities for innovative business models and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
Technologies Underpinning Web 3.0:
- Blockchain: At the heart of Web 3.0 lies blockchain technology, a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Blockchain provides the foundation for decentralized applications (dApps), digital currencies, and smart contracts, enabling secure and transparent data management.
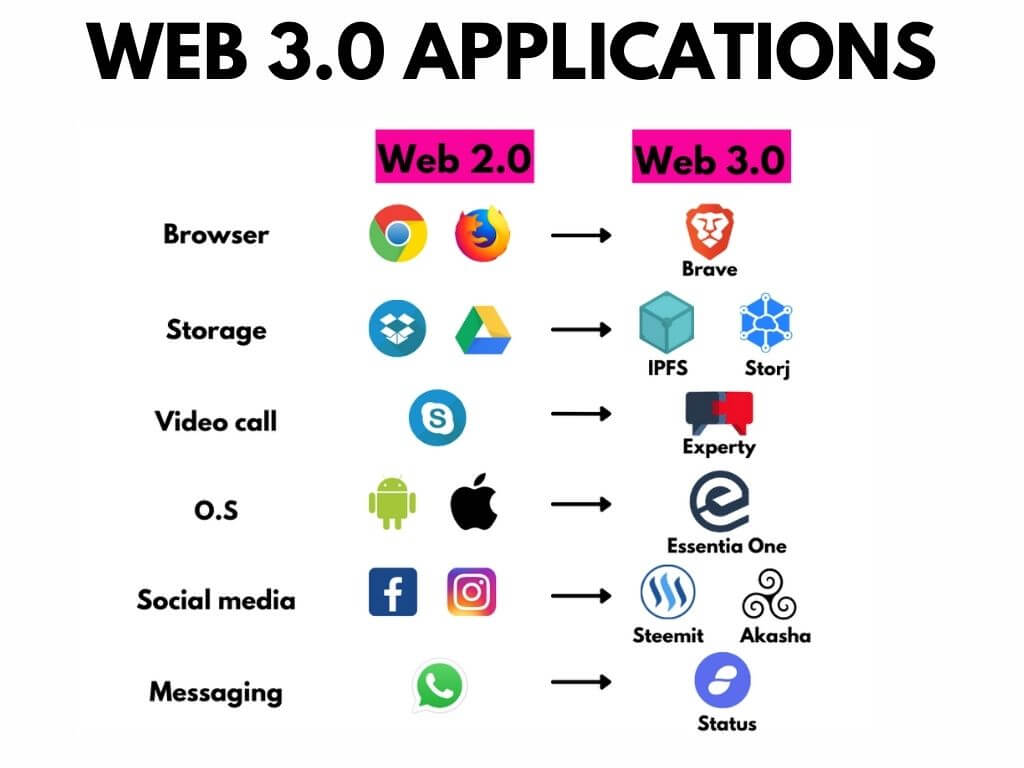
- Decentralized Storage: Web 3.0 leverages decentralized storage solutions such as IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) and Filecoin to store and retrieve data in a distributed manner. By eliminating central points of failure and censorship, decentralized storage enhances data resilience and accessibility.
- Cryptographic Identity: Cryptographic identity systems such as decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials enable users to establish and manage their digital identities in a secure and privacy-preserving manner. These systems empower individuals to control access to their personal information and authenticate themselves across various online services.
- Oracles: Oracles serve as bridges between blockchain networks and the external world, providing smart contracts with access to real-world data and events. By interfacing with external APIs and data feeds, oracles enable smart contracts to execute logic based on real-time information, opening up new possibilities for decentralized applications.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Web 3.0 relies on consensus mechanisms such as proof of work (PoW), proof of stake (PoS), and delegated proof of stake (DPoS) to validate and secure transactions on blockchain networks. These consensus algorithms ensure network integrity and incentivize participants to contribute to the network’s operation.
Applications of Web 3.0:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms leverage blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management without intermediaries. DeFi protocols such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending platforms offer users greater financial autonomy and accessibility.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs represent unique digital assets that are indivisible and verifiable on blockchain networks. From digital art and collectibles to virtual real estate and gaming assets, NFTs enable ownership and trading of digital assets in a decentralized manner.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): DAOs are decentralized organizations governed by smart contracts and governed by token holders. DAOs enable collective decision-making, resource allocation, and governance without centralized control, fostering community-driven initiatives and collaborations.
- Supply Chain Management: Web 3.0 facilitates transparent and traceable supply chain management through blockchain-based solutions. By recording transactions and events on a tamper-proof ledger, blockchain enhances supply chain visibility, accountability, and efficiency.
- Digital Identity Management: Web 3.0 empowers individuals to take control of their digital identities through self-sovereign identity solutions. By leveraging cryptographic techniques and decentralized networks, users can securely manage their identities and authenticate themselves across various online platforms.
Implications of Web 3.0:
- Disintermediation: Web 3.0 disrupts traditional intermediaries and gatekeepers, enabling direct peer-to-peer interactions and transactions. This disintermediation reshapes industries and business models, empowering individuals and reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
- Data Privacy and Security: With greater emphasis on user control and cryptographic security, Web 3.0 enhances data privacy and security. By decentralizing data storage and implementing cryptographic identity solutions, Web 3.0 mitigates risks associated with centralized data breaches and surveillance.
- Economic Inclusion: Web 3.0 fosters economic inclusion by providing access to financial services and opportunities for underserved populations. From microtransactions and remittances to crowdfunding and decentralized lending, Web 3.0 democratizes access to finance and fosters financial inclusion on a global scale.
- Innovation and Experimentation: Web 3.0 catalyzes innovation and experimentation across various domains, from finance and governance to art and entertainment. Decentralized technologies and open protocols enable developers and entrepreneurs to explore new frontiers and build innovative solutions without permission or barriers.
- Regulatory Challenges: The decentralized nature of Web 3.0 presents regulatory challenges for governments and policymakers. Balancing innovation with consumer protection and regulatory compliance remains a key challenge in the evolving regulatory landscape of Web 3.0.
Conclusion:
In the grand tapestry of technological evolution, Web 3.0 stands as a pivotal chapter, heralding a new era of decentralized innovation and digital sovereignty. As we traverse the landscape of blockchain-powered ecosystems, cryptographic identities, and decentralized applications, the possibilities for transformative change are boundless.
Web 3.0 embodies the principles of decentralization, interoperability, and user empowerment, reshaping the internet from a centralized entity into a distributed network of trust and collaboration. By harnessing the collective potential of blockchain technology, smart contracts, and cryptographic primitives, Web 3.0 pioneers a path towards greater transparency, security, and autonomy in the digital realm.
Yet, amidst the promise of Web 3.0 lie formidable challenges and uncertainties. Regulatory frameworks must adapt to the decentralized nature of these emerging technologies, striking a delicate balance between innovation and accountability. Technical hurdles such as scalability, interoperability, and user experience demand innovative solutions and collaborative efforts from industry stakeholders.
Moreover, the transition to Web 3.0 requires a cultural shift towards digital literacy, sovereignty, and ethical stewardship. As individuals navigate the complexities of decentralized finance, digital identity management, and peer-to-peer interactions, education and awareness become paramount in fostering responsible participation in the decentralized ecosystem.

In this era of rapid technological advancement, the future of Web 3.0 is shaped not only by the ingenuity of developers and entrepreneurs but also by the values and aspirations of society at large. By embracing the principles of decentralization, inclusivity, and resilience, we can collectively chart a course towards a more equitable, transparent, and empowering digital future.
As we embark on this journey into the decentralized frontier, let us tread with curiosity, humility, and a steadfast commitment to building a Web 3.0 that serves the needs of humanity, fosters innovation, and upholds the values of freedom, privacy, and dignity for all. In the crucible of decentralization, we have the opportunity to redefine the internet as a force for positive change, unlocking new possibilities and shaping a world where sovereignty resides in the hands of the many, not the few.